Date de publication
2023-09-05
Introduction to Database Enrichment
Businesses and organizations rely heavily on their databases to make informed decisions, personalize customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. However, not all databases are created equal. Many databases suffer from data quality issues, incomplete information, and outdated records. This is where database enrichment comes into play, offering a solution to enhance the value and accuracy of your database. This blog will explore the world of database enrichment, its benefits, methods, strategies, practical applications, challenges, and future trends.
Understanding Database Enrichment
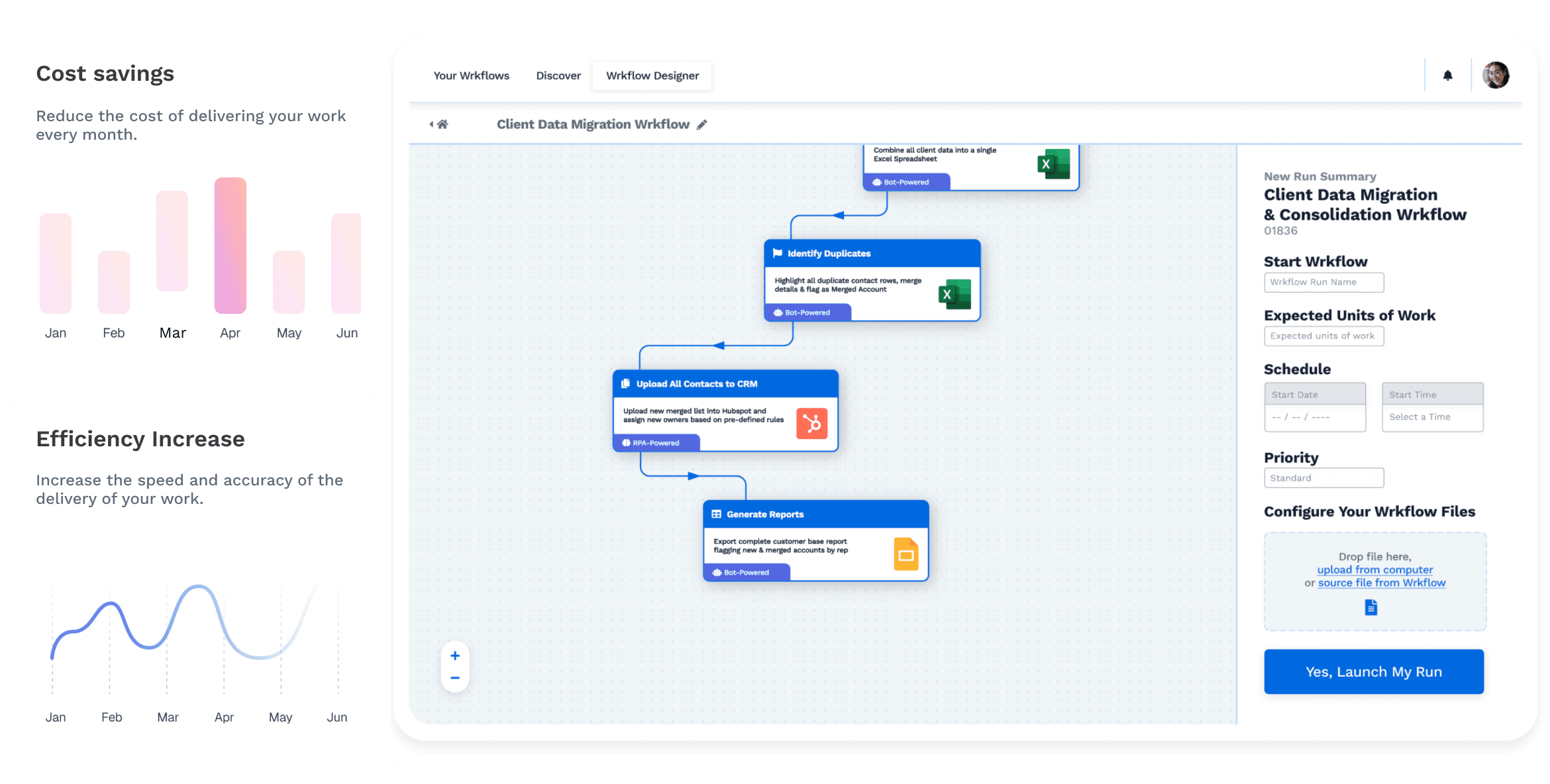
At its core, database enrichment is enhancing your existing database by adding new, valuable data or refining existing data to improve its quality and completeness. This can be achieved through various methods tailored to specific data needs. One standard process involves integrating data from external sources, such as providers and APIs. These sources can provide additional information about your customers, prospects, or products, allowing you to gain deeper insights.
The benefits of database enrichment are far-reaching. Improved data quality ensures more accurate analytics, better decision-making, and a stronger foundation for data-driven strategies. With enriched data, you can segment your audience more effectively, personalize marketing efforts, and target your resources where they will have the most impact.
Types of Data Enrichment Methods
External Data Sources: External data sources are a goldmine for enriching your database. Data providers and APIs can offer a wide range of data, from demographic and firmographic information to social media profiles and geospatial data. Integrating data from these sources gives you a more comprehensive view of your customers or prospects.
Data Cleansing and Validation: Data quality is paramount in database enrichment. Removing duplicates, standardizing data formats, and validating information is crucial to ensure your database is accurate and reliable. Data cleansing tools can help automate this process.
Geospatial Enrichment: Location-based data is invaluable for many businesses. Geocoding and reverse geocoding can help you pinpoint the exact locations of your customers or assets. This is particularly useful for companies with physical stores or field operations.
Social Media and Online Enrichment: Social media profiles and web scraping can provide valuable insights into customers' online behaviour, interests, and preferences. This information can be used to tailor marketing campaigns and improve customer engagement.
Demographic and Firmographic Enrichment: Understanding your customers' or prospects' demographics and firmographics is essential for targeted marketing. Enriching your database with this information allows you to create more relevant and personalized content.
Strategies for Effective Database Enrichment
Successful database enrichment requires a well-thought-out strategy. Here are some key strategies to consider:
Define Your Enrichment Goals: Start by identifying the specific data deficiencies in your database and setting clear objectives. What do you hope to achieve through enrichment? Are you looking to understand your customer demographics better or improve the accuracy of contact information?
Selecting the Right Data Sources: Choose reputable data providers and APIs that align with your goals. Ensure that the data you acquire complies with privacy regulations and is up-to-date.
Data Integration and Automation: Implement data integration tools and automate the enrichment process as much as possible. This reduces manual work, minimizes errors, and ensures your database stays current.
Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance: Enrichment is an ongoing process. Regularly update your database with new information and perform quality checks to promptly identify and rectify any issues.
Data Security and Privacy Considerations: In an era of heightened data privacy concerns, it's crucial to prioritize the security of the data you collect and enrich. Implement encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information and comply with regulations like GDPR.
Practical Applications of Database Enrichment
The applications of enriched databases are vast and varied. Here are a few practical examples:
Sales and Marketing: Enriched data can help sales teams segment customers more effectively, prioritize leads based on various criteria, and tailor marketing campaigns to specific demographics or interests.
E-commerce and Personalization: E-commerce platforms can use enriched data to make product recommendations based on customer behaviour and preferences, enhancing the user experience and driving sales.
Healthcare and Medical Research: In healthcare, patient data enrichment can improve patient care, aid in disease tracking, and support medical research by providing comprehensive patient histories and demographics.
Finance and Risk Assessment: Financial institutions can use enriched data for credit scoring, fraud detection, and risk assessment. They can make more accurate lending decisions by analyzing a broader set of data points.
Challenges and Considerations
While database enrichment offers numerous benefits, it has its challenges. Here are some considerations:
Data Accuracy and Reliability: Enriched data is only valuable if accurate. Relying on unreliable or outdated sources can lead to erroneous insights and decisions.
Cost and Budget Constraints: Enrichment can be costly, especially when dealing with large databases or premium data sources. Organizations must balance the cost of enrichment with the expected return on investment.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns: Data enrichment raises ethical questions about data privacy and consent. Handling customer data with care and transparency is essential, complying with privacy regulations.
Data Governance and Compliance: Organizations must establish robust data governance practices to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Integration Complexity: Integrating external data sources into existing databases requires technical expertise and well-designed data pipelines.
Future Trends in Database Enrichment
The world of database enrichment is continually evolving. Here are some future trends to watch for:
AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and machine learning algorithms will play a more significant role in data enrichment, automating decision-making processes, and improving the accuracy of data matching and validation.
Blockchain for Data Provenance: Blockchain technology can enhance data provenance, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of enriched data. This can be particularly important in industries where data trust is critical.
Enhanced Automation and Scalability: Enrichment processes will become more automated and scalable, allowing organizations to handle large volumes of data efficiently.
Evolving Data Privacy Regulations: As data privacy regulations continue to evolve, organizations must adapt their enrichment practices to comply with new requirements.
Final Say
Database enrichment is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to optimize their databases and harness the full potential of their data. By understanding the various methods, strategies, and applications of database enrichment, businesses can make more informed decisions, provide better customer experiences, and stay competitive in a data-centric world. While challenges and ethical considerations must be addressed, the future of database enrichment looks promising, with advanced technologies and evolving best practices shaping its trajectory.
Start Automating with Wrk
Kickstart your automation journey with the Wrk all-in-one automation platform