Date de publication
2023-07-13
Introduction to Warehouse Management System (WMS) Integration
Warehouse management system (WMS) integration is vital in modern warehouse operations. WMS integration optimizes warehouse processes, improves efficiency, and enhances overall productivity by seamlessly connecting various components and systems. This comprehensive guide provides an overview of WMS integration, its importance, benefits, and challenges.
Understanding Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
A warehouse management system is a software application designed to manage and control warehouse operations. It handles crucial functions such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipping. WMS acts as a central hub, streamlining processes, optimizing resource allocation, and providing real-time visibility into warehouse activities.
The Need for Integration in Warehouse Management Systems
Integration is essential to achieving seamless warehouse operations. By integrating various systems with WMS, such as inventory management, order processing, and shipping, organizations can eliminate silos, reduce manual data entry, and enhance data accuracy. The integration allows for smooth information flow, enabling real-time updates and improving decision-making processes.
Types of Integration in Warehouse Management Systems
1. Application Programming Interface (API) integration:
API integration allows different systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and e-commerce platforms, to communicate with the WMS. It facilitates data exchange and enables real-time synchronization, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing errors. Best practices for successful API integration involve understanding API documentation, establishing error-handling mechanisms, and conducting thorough testing.
2. EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) integration:
EDI enables electronic data exchange between trading partners. In the context of WMS integration, EDI facilitates seamless communication and data transfer between the WMS and external systems. It eliminates manual data entry, accelerates order processing, and improves supply chain visibility. Common EDI standards used in warehouse management include ANSI X12 and EDIFACT.
3. IoT (Internet of Things) integration:
IoT integration involves connecting IoT devices and sensors to the WMS. This integration enables real-time inventory tracking, monitoring environmental conditions, and automating processes. For example, RFID tracking allows for accurate inventory tracking, while real-time inventory monitoring ensures timely replenishment. Implementing IoT integration requires careful planning, addressing security concerns, and selecting suitable IoT devices for specific warehouse needs.
Key Considerations for Successful WMS Integration
Requirements and Goals
Identifying business requirements and integration goals is a crucial first step in WMS integration. By clearly understanding the specific needs and objectives of the organization, businesses can align their integration strategy with their overall goals. This involves identifying pain points in existing processes, determining the desired integration outcomes, and establishing measurable metrics to evaluate success.
System Compatibility
Assessing system compatibility and data mapping is essential to ensure seamless data exchange and integration. Evaluation includes assessing technical aspects such as data formats, protocols, and APIs. Additionally, data mapping is critical for defining how data will be transferred, transformed, and synchronized between systems.
Data Security and Privacy
Establishing robust data security and privacy measures is vital when integrating WMS with other systems. Warehouse operations involve handling sensitive customer data, inventory details, and financial records. Organizations must implement stringent security measures to protect this data from unauthorized access, breaches, and potential vulnerabilities.
Scalability
Planning for scalability and future system updates is necessary to accommodate evolving business needs. Technology is constantly evolving, and system updates and enhancements are inevitable. Organizations should plan for these updates, evaluate the upgrade process, and ensure compatibility with integrated systems.
Trusted Vendors and Partners
Collaborating with vendors and technology partners who specialize in WMS integration can provide valuable expertise, guidance, and support throughout the integration process. This collaboration ensures a smoother integration process, reduces implementation risks, and enables organizations to leverage the expertise of those who have successfully executed similar integration projects.
Infrastructure Limitations
Infrastructure limitations, such as network bandwidth constraints or hardware limitations, can impact the performance and scalability of integrated systems. Conducting a thorough infrastructure assessment and investing in necessary upgrades or optimizations is crucial to support the integrated systems.
Change Management Strategy
Effective change management practices are essential to ensure smooth employee adoption during WMS integration projects. Organizations should develop a comprehensive change management plan with clear communication, training programs, and user engagement initiatives.
By addressing these common challenges through proactive strategies, organizations can overcome obstacles and ensure the success of their WMS integration projects. It is important to anticipate potential challenges, plan accordingly, and leverage the expertise of integration partners to find optimal solutions.
Future Trends in WMS Integration
Emerging technologies heavily influence future trends in WMS integration, offering exciting possibilities for warehouse optimization:
AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various systems, enabling intelligent decision-making and optimization.
ML algorithms can learn from historical data to predict demand patterns, optimize inventory levels, and automate replenishment processes.
Automation technologies, such as robotic process automation (RPA), can automate repetitive tasks like order processing, inventory counting, and picking, reducing manual effort and improving operational efficiency.
By leveraging these technologies, WMS integration can achieve unprecedented efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability.
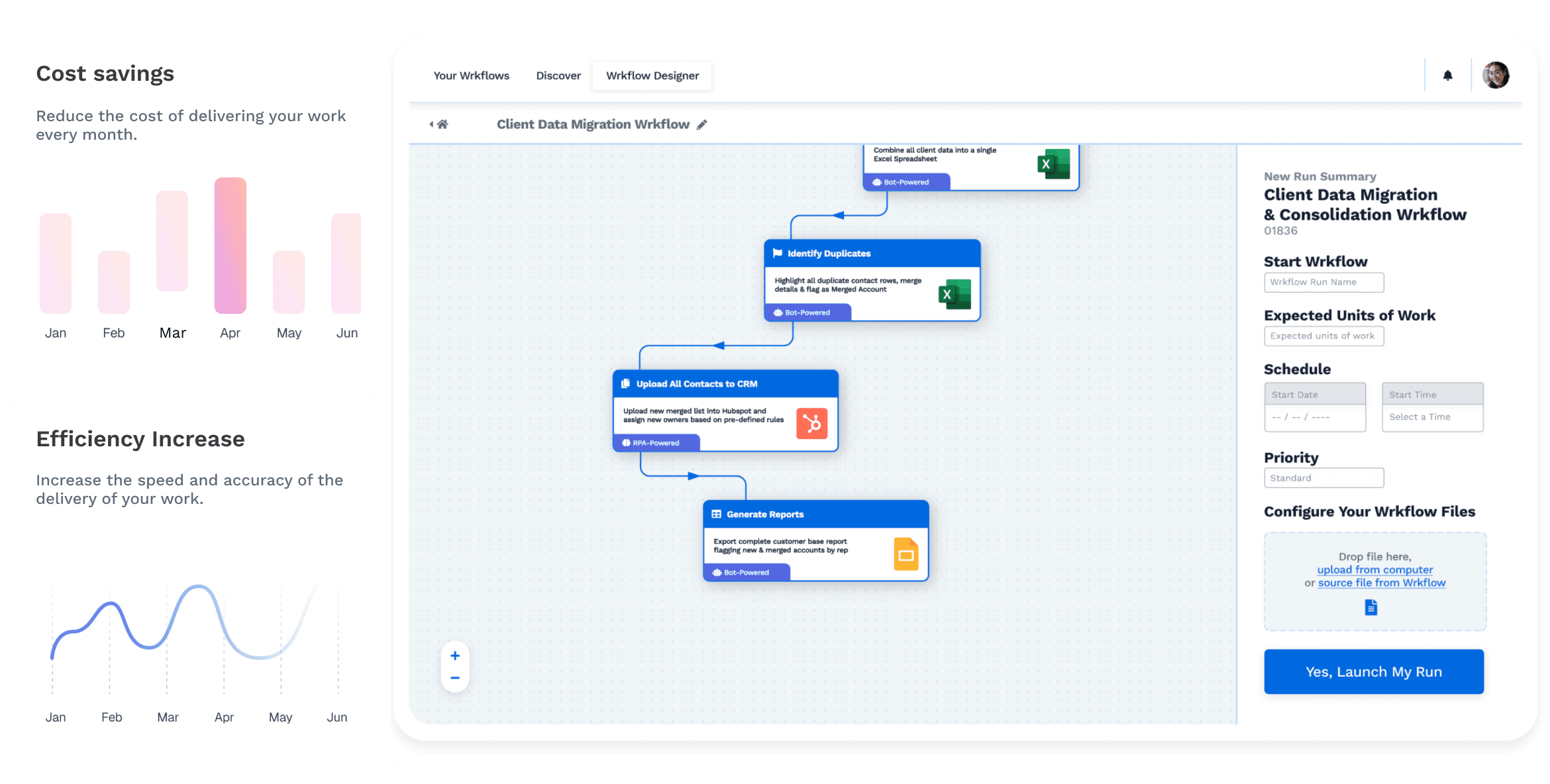
Start Automating with Wrk
Kickstart your automation journey with the Wrk all-in-one automation platform