Publish Date
2024-01-09
Overview
The need for seamless connectivity among various business applications is more crucial than ever. Organizations rely on many software solutions for different aspects of their operations, the challenge lies in efficiently integrating these systems to ensure a smooth flow of data and processes. This blog explores the intricacies of application integration, its benefits to businesses, common integration patterns, key considerations, steps in navigating integration, real-world case studies, and future trends in this dynamic landscape.
Introduction
Application integration has become a cornerstone for the success of modern businesses. At its core, application integration connects different software applications to function harmoniously and share data seamlessly. This connectivity is vital as companies utilize a variety of applications, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems, each serving a specific purpose. Navigating the complexities of application integration is essential for organizations aiming to harness the full potential of their technology stack.
Types of Business Applications
Before delving into the integration process, it's crucial to understand the types of business applications that organizations commonly use. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems streamline core business processes, while Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems focus on managing customer interactions. Supply Chain Management (SCM) systems optimize the flow of goods and services, and Human Resource Management (HRM) systems handle workforce-related functions. Recognizing the diversity of these applications lays the foundation for effective integration strategies.
Benefits of Application Integration
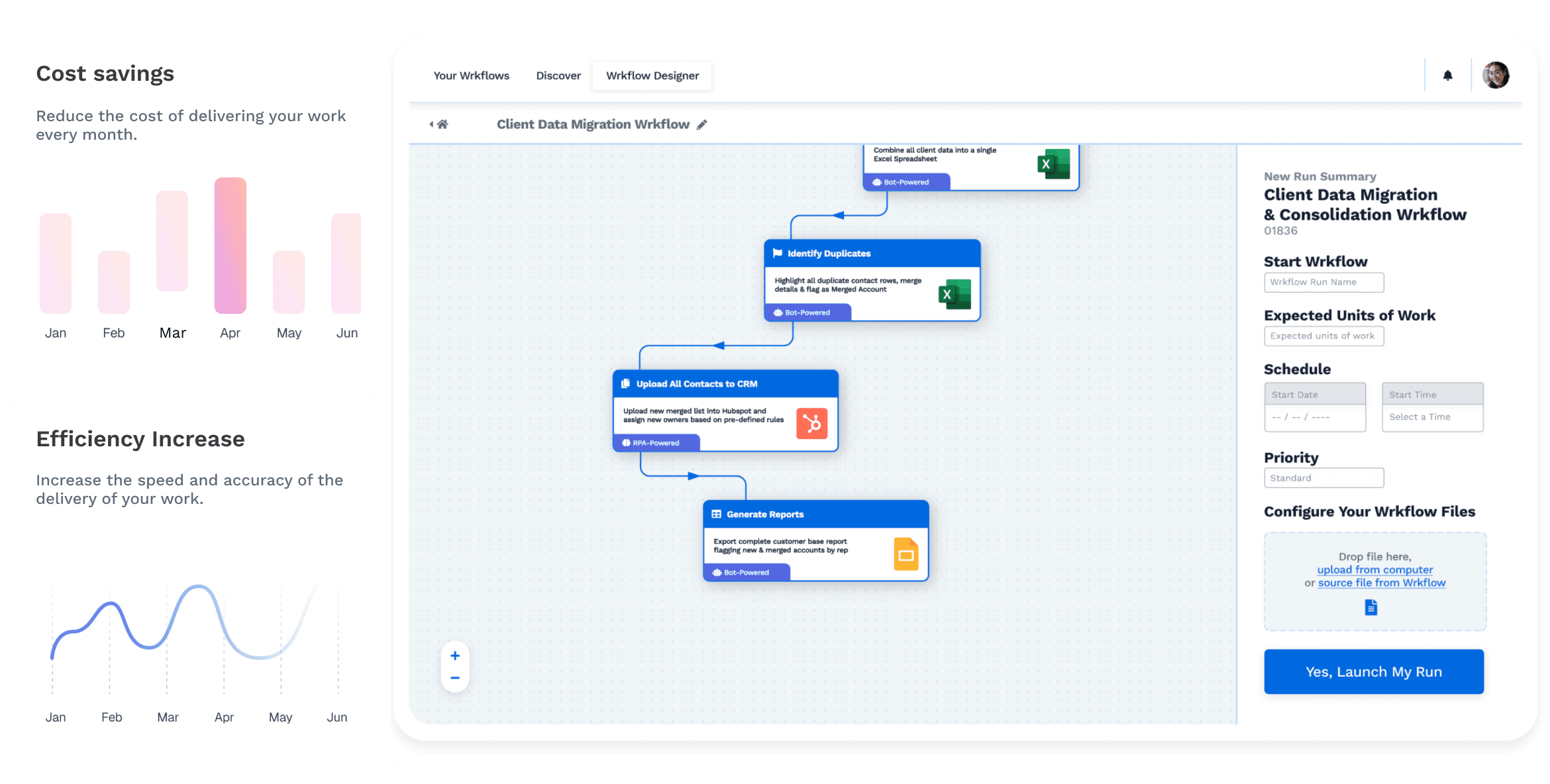
The advantages of application integration are multifaceted and touch every aspect of business operations. Improved data accuracy and consistency ensure that decisions are based on reliable information, enhancing operational efficiency. Seamless communication and collaboration between different departments become possible, fostering a more connected and productive workplace. Real-time decision-making facilitates organizations to respond swiftly to changing market conditions. Ultimately, integrating business applications contributes to significant cost savings over time.
Common Integration Patterns
Various integration patterns exist, each offering distinct approaches to connecting applications. Point-to-point integration involves establishing direct connections between individual applications. Hub-and-spoke integration employs a centralized hub communicating with satellite applications, simplifying connection management. Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) is an intermediary for communication between applications, while API integration leverages standardized interfaces to connect different systems. Middleware solutions provide a platform for seamless data exchange between applications.
Key Considerations in Application Integration
Successfully navigating application integration requires careful consideration of several vital factors. Compatibility and interoperability are paramount, ensuring that different applications can work together cohesively. Data mapping and transformation processes must be defined to bridge data formats and structure disparities. Security and compliance are non-negotiable, especially when dealing with sensitive business information. Scalability and flexibility are crucial to accommodate future growth and evolving business needs. User experience and accessibility round out the considerations, as integration solutions should be user-friendly and accessible to all relevant stakeholders.
Steps in Navigating Application Integration
Assessing Integration Needs and Objectives: Organizations must clearly define their integration needs and objectives before embarking on the integration journey. It involves understanding the specific business processes that require integration and establishing the desired outcomes.
Choosing the Right Integration Approach: With a clear understanding of integration needs, organizations can then choose the most suitable integration approach. Whether it's point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, ESB, API, or middleware, the choice depends on factors such as the complexity of the integration, budget constraints, and scalability requirements.
Selecting Integration Technologies and Tools: Once the approach is decided, selecting the right technologies and tools is critical. This involves considering factors such as the compatibility of the tools with existing systems, their ease of use, and the level of support provided.
Designing and Planning Integration Architecture: The integration architecture is developed in the design and planning phase. This includes mapping out how different applications interact, defining data flow, and establishing protocols for error handling and synchronization.
Implementing and Testing Integration Solutions: The implementation phase begins with the architecture in place. Integration solutions are deployed, and thorough testing ensures that data flows seamlessly between applications and that the integrated system operates as intended.
Monitoring and Maintaining Integration Processes: Post-implementation, continuous monitoring is crucial to identify and address any issues promptly. Regular maintenance ensures the integration remains robust and adapts to changes in the business environment or technology landscape.
Future Trends in Application Integration
As technology evolves, so do trends in application integration. Cloud-based integration is gaining prominence, offering greater flexibility and scalability. The integration landscape is also witnessing the integration of emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain. Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI) significantly automates and optimizes integration processes, making them more intelligent and adaptive.
Final Say
In conclusion, navigating application integration is critical for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age. The benefits are substantial, ranging from improved operational efficiency to cost savings and enhanced decision-making. Organizations can successfully navigate the integration process by understanding the types of business applications, selecting the proper integration patterns, and considering key factors. Real-world case studies and a glimpse into future trends underscore the importance of staying abreast of developments in the dynamic field of application integration. Embracing these strategies will position businesses for success in an increasingly interconnected and technologically driven world.
Start Automating with Wrk
Kickstart your automation journey with the Wrk all-in-one automation platform