Publish Date
12/12/2024
Business Process Automation (BPA) has become a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes, especially for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that seek to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and stay competitive. Implementing BPA doesn’t have to be overwhelming or complex, and with the right approach, businesses can start reaping the benefits quickly. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you begin automating your business:
Step 1: Identify the Processes to Automate
The first step in automating your business is identifying the processes that will benefit the most from automation. Look for tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, and prone to human error. These tasks are prime candidates for automation. Common areas for automation in small businesses include invoicing, payroll, data entry, customer service, email marketing, and inventory management. Conduct a thorough audit of your business operations, asking questions like:
Which tasks take up a lot of employee time?
Where do bottlenecks or delays occur most often?
Are there recurring processes that can be standardized?
Once you’ve identified these processes, prioritize them based on their impact on your business. Start with the low-hanging fruit—tasks that can be automated easily with immediate benefits.
Step 2: Choose the Right Automation Tools
Once you know what processes you want to automate, the next step is selecting the right tools for the job. The market offers a wide range of automation platforms, and it’s crucial to choose one that aligns with your business needs, budget, and existing infrastructure. Many BPA tools are user-friendly and designed specifically for small and medium businesses. Look for features like:
Easy integration with your current software (e.g., CRM, accounting software, email platforms).
Customizable workflows that can be tailored to your business processes.
Scalability, so the tool can grow with your business.
Good customer support and a strong user community.
Some popular BPA tools for small businesses include Zapier, HubSpot, Monday.com, and QuickBooks for automating workflows, marketing, and accounting processes.
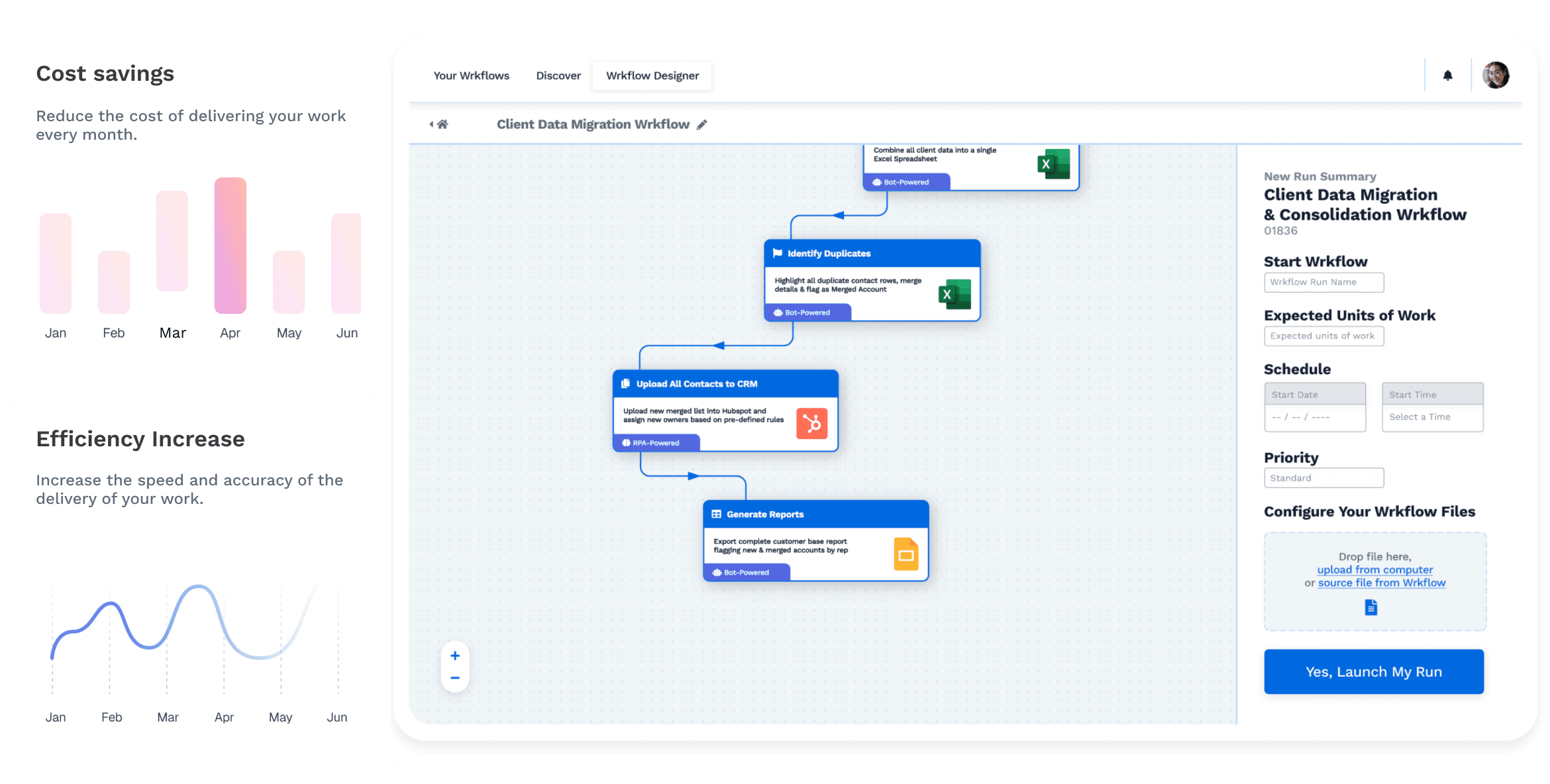
Step 3: Map Out Your Workflow
Before implementing the automation tool, it’s important to map out your workflows. This means defining the steps in the process that you want to automate. Create a flowchart or document that outlines the current manual process, and then design an optimized version that integrates automation. For example, in automating an invoice process, you might map out the steps:
The customer places an order.
Invoice is generated and sent manually.
Payment is tracked and logged.
A follow-up reminder is sent.
Then, using BPA tools, you can automate actions like sending the invoice once the order is placed or setting reminders for unpaid invoices after a certain number of days. Mapping out the workflow ensures you understand the process inside out, which helps in selecting the right automation triggers.
Step 4: Test Your Automation
Before fully rolling out your BPA system, it’s crucial to run tests to ensure the automated process works as expected. Run through different scenarios and make sure that the automation tool triggers the right actions at the right time. For example, if you’re automating your sales process, test that the system sends the correct email responses to prospects and updates the CRM database with accurate information. Testing the system will help you identify any glitches or areas for improvement before you implement it across your entire business.
Step 5: Train Your Team
Automation will only be successful if your team understands how to use it effectively. Training your team is an essential part of the implementation process. Ensure that everyone involved is familiar with the new automated workflows and understands how to leverage the tools. This training could include showing employees how to handle exceptions, monitor automation outcomes, and intervene if needed. Even though automation minimizes manual tasks, human oversight is often required to ensure the system runs smoothly.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize
Once your automation system is up and running, don’t forget to monitor its performance and make improvements over time. BPA is not a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process of optimization. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as time saved, cost reductions, and employee productivity to measure the success of automation. Use this data to refine your workflows, adjust automation triggers, and add new tasks to the automation pipeline. As your business grows, new processes will emerge, and automation can evolve to meet these needs.
Step 7: Scale Your Automation
As your business expands, you’ll find new areas where automation can create efficiencies. The beauty of BPA tools is that they are scalable, allowing you to automate more complex workflows or new processes without the need for a major overhaul. Gradually, you can automate customer communications, sales processes, reporting, and more. This scaling process ensures that you maintain smooth operations as your business grows, all while keeping overhead costs low.
Start Automating with Wrk
Kickstart your automation journey with the Wrk all-in-one automation platform