Publish Date
2023-11-03
Automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency and productivity. Two prominent approaches to automation have emerged in recent years: Traditional Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Each has its unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations. In this blog, we will unravel the critical differences between RPA and Traditional Automation to help you make informed decisions when considering automation solutions for your business.
Understanding Traditional Automation
Traditional automation refers to using computer programs and technology to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks within an organization. These tasks often involve data entry, calculations, and basic decision-making processes. Traditional automation has existed for several decades, with businesses relying on software applications and custom coding to streamline their processes.
One of the earliest examples of traditional automation is using spreadsheets and macros to automate data manipulation and reporting. While traditional automation has served businesses well over the years, it has limitations. It is primarily designed to execute pre-defined tasks and lacks the adaptability to handle complex, dynamic processes.
Advantages of traditional automation include accuracy and the ability to work with existing systems and infrastructure. However, it may require a significant investment in development and maintenance, making it less agile in responding to changing business needs.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
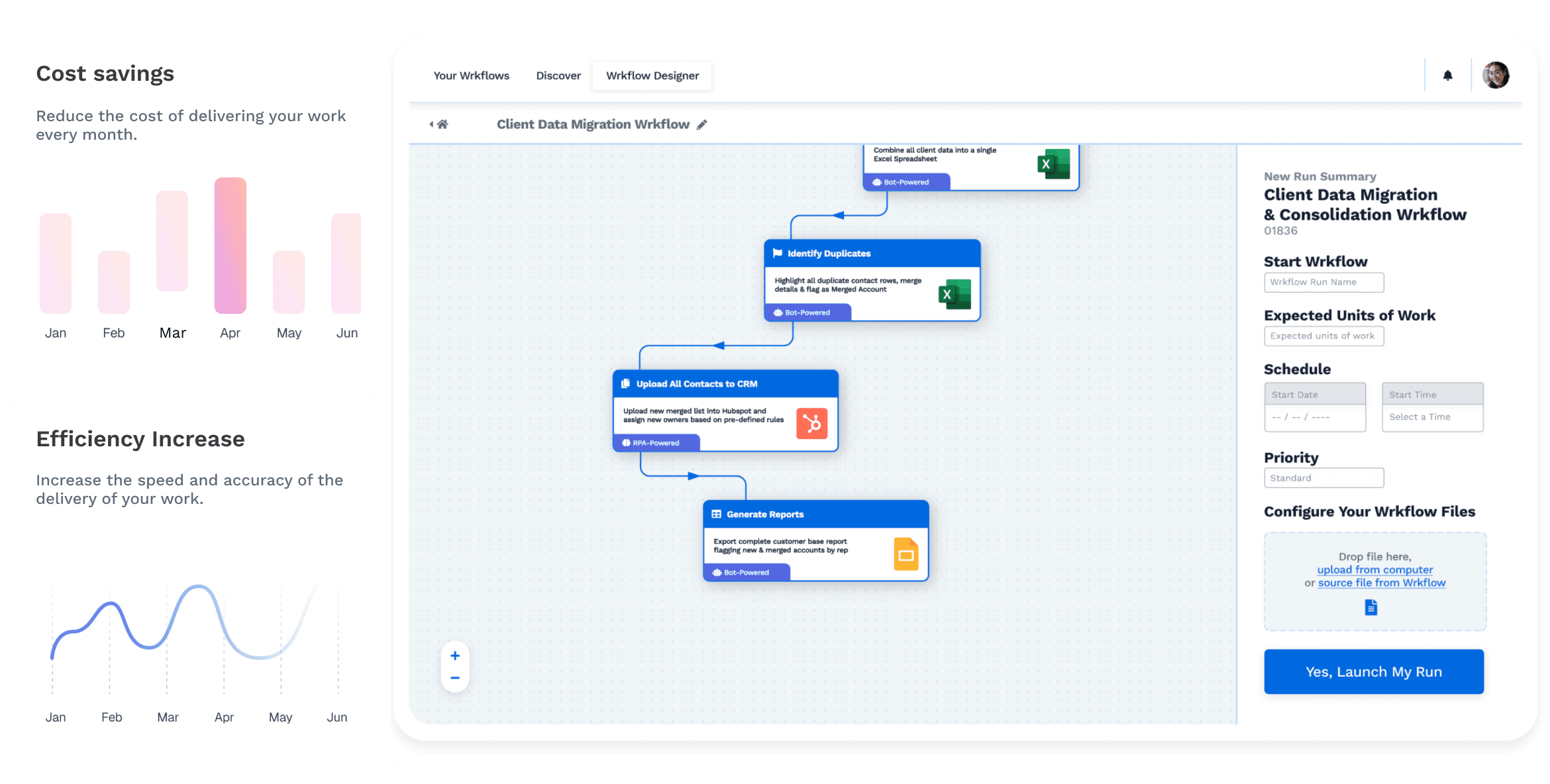
Robotic Process Automation (RPA), on the other hand, is a more recent development that leverages specialized software robots (or "bots") to mimic human interactions with digital systems. RPA can be applied to a wide range of tasks, from data entry and data extraction to more complex activities like report generation and customer interactions. RPA systems are designed to be user-friendly and do not require extensive coding or programming skills.
One of the key benefits of RPA is its ability to interact with existing software applications through their user interfaces, just like a human employee would. RPA bots can navigate applications, extract and input data, and perform tasks without changing the underlying systems. This adaptability makes RPA well-suited for a variety of industries and processes.
However, RPA also has its drawbacks, including limitations in handling unstructured data and a reliance on the stability of the user interfaces it interacts with. Complex decision-making and cognitive tasks are outside the scope of RPA, which is more focused on automating rule-based, repetitive activities.
Key Differences Between RPA and Traditional Automation
Technology and Tools:
Traditional Automation: Typically relies on custom coding and script-based approaches.
RPA: Utilizes specialized RPA software tools with user-friendly interfaces, making automation accessible to more users.
Deployment and Implementation:
Traditional Automation: Requires significant development effort, customization, and integration with existing systems.
RPA: Can be rapidly deployed with minimal disruption to existing systems, as it interacts through user interfaces.
Adaptability and Scalability:
Traditional Automation: Less flexible and may require significant modifications when business processes change.
RPA: Highly adaptable and scalable, able to handle variations in processes and volumes of work.
Human Involvement:
Traditional Automation: Typically involves human intervention during design, implementation, and maintenance.
RPA: Requires less technical expertise, enabling business users to build and manage automation processes.
Use Cases and Industry Examples
Traditional automation has been prevalent in industries such as manufacturing and finance. In manufacturing, automation has been used for tasks like assembly line automation, quality control, and inventory management. In the finance sector, traditional automation has been crucial for automating account reconciliations, financial reporting, and transaction processing.
RPA, on the other hand, has found its place in healthcare, where it streamlines patient data management, insurance claims processing, and appointment scheduling. In customer service, RPA is utilized for chatbots, email automation, and service ticket management. The adaptability and ease of use make RPA an attractive solution for industries that require frequent changes and improvements in their processes.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Another significant difference between RPA and traditional automation is their integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). While traditional automation can incorporate AI and ML to some extent, RPA can seamlessly integrate these technologies. RPA systems can be enhanced with AI algorithms to make decisions based on data analysis, enabling even more advanced automation capabilities.
The synergy between RPA and AI/ML is beneficial in industries where data-driven decisions and predictive analytics are essential. For example, in finance, RPA can be combined with AI to perform credit risk assessments, while in healthcare, RPA can assist in patient data analysis and diagnosis predictions.
Cost Analysis
Regarding costs, traditional automation tends to have higher initial setup and maintenance expenses. Developing custom automation solutions, integrating them with existing systems, and maintaining the codebase can be resource-intensive. On the other hand, RPA, with its user-friendly tools and adaptability, often leads to lower upfront costs.
However, it's important to consider the long-term cost implications. Traditional automation may require less ongoing maintenance and license fees, while RPA could incur higher costs as the number of bots and the complexity of automation processes increase. The cost analysis will vary depending on the specific needs and circumstances of each business.
ROI and Efficiency Gains
Assessing the return on investment (ROI) for both traditional automation and RPA is crucial. Traditional automation can offer significant ROI by reducing manual labour, improving accuracy, and increasing throughput. However, it may take a longer time to achieve these benefits due to the initial development and implementation stages.
RPA, on the other hand, can provide a rapid ROI due to its ease of deployment and adaptability. Bots can be quickly configured to perform tasks, leading to efficiency gains and cost savings in a shorter timeframe. The specific ROI will depend on the processes automated, the scale of implementation, and the industry in which it is applied.
Future Trends and Predictions
Looking to the future, we can anticipate several trends in the world of automation. Traditional automation will continue to play a vital role in industries where stability and predictability are paramount. Industries like manufacturing and utilities will benefit from more efficient and streamlined processes.
RPA, on the other hand, is likely to see increased adoption in industries requiring flexibility and adaptability, such as customer service and healthcare. Integrating AI and ML will further enhance the capabilities of RPA, enabling more intelligent decision-making and predictive analytics.
Final Say
RPA and traditional automation have their places in the business world, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs and circumstances of an organization. Traditional automation is well-suited for stable, rule-based processes, while RPA excels in dynamic, adaptable environments. As technology advances, the lines between these two approaches may blur, creating even more powerful automation solutions for businesses in the future. Ultimately, the key is understanding your business needs and objectives to make an informed choice regarding which automation approach to adopt.
Start Automating with Wrk
Kickstart your automation journey with the Wrk all-in-one automation platform